answered by nchi (4k points) selected by Darshee Best answer u = x3 y3 3xy2 ∴ u is a homogeneous function in x and y of degree 3 ∴ By Euler's theorem, = 3u Hence Euler's theorem is verified1) is a critical point The second derivative test f xx = 2;f yy = 2;f xy = 0 shows this a local minimum withShowthatu(x,y) = 2x−x33xy2 isharmonic on R2 and find a harmonic conjugate v(x,y) for it Solution Define f(z) = 2z − z3 This function is analytic on C f(xiy) = 2(xiy)−(xiy)3 = 2x2iy−(x33x2iy3xi2y2i3y3) = 2x−x33xy2i(2y−3x2yy3) We have that the real part of f(z) is u(x,y), and hence it is harmonic on R2 Also v(x,y
1
If u(x y)=x^2 y^2 2x-3xy then
If u(x y)=x^2 y^2 2x-3xy then-Y^2 at the point a) ( 2, 1, 3), b) ( 0Theorem 2 Let u(x;y) be harmonic in some neighbourhood of the point (x 0;y 0) Then, there exists a conjugate harmonic function v(x;y) de ned in the neighbourhood, and f(z) = u(x;y) iv(x;y) is an analytic function Proof The harmonic function u(x;y) and it conjugate harmonic function v(x;y) will satisfy the CR equations u x = v y and u




Solve The Equation X 2 3xy Y 2 Dx X 2dy 0 Given That Y 0 And X 1
the table you have that U(X, Y) = 10 So since U(X, Y) = XY you have XY = 10 What combination of X and Y will make this equation true?Find one factor of the form x^{k}m, where x^{k} divides the monomial with the highest power x^{2} and m divides the constant factor 3y^{2} One such factor is x3y Factor the polynomial by dividing it by this factor(b) 2 x y dx ( y 2 x 2) dy = 0 Here, M = 2 x y, M y = 2x, N = y 2 x 2, and N x = 2 xNow, ( N x M y) / M = ( 2 x 2 x ) / ( 2 x y) = 2 / yThus, μ = exp ( ∫ 2 dy / y ) = y2 is an integrating factor The transformed equation is ( 2 x / y ) dx ( 1 x 2 y2) dy = 0 Let m = 2 x / y, and n = 1 x 2 y2Then, m y = 2 x y2 = n x, and the new differential equation is exact
(x y)2 (x y)3 (x y)2 (x y)3 c) fx = −2xsin(x2 y), fxy = (fx)y = −2xcos(x2 y);MATH 42 (1516) partial diferential equations CUHK 8Note that u(x;y) = ex2y=4 is a special solution of te inhomogeneous equation, and by the result of 128 above, the general solution of the corresponding homogeneous equation is f(x y)e (xy)=2Thus theConsider 2x^ {2}3xy2y^ {2}2x11y12 as a polynomial over variable x Find one factor of the form kx^ {m}n, where kx^ {m} divides the monomial with the highest power 2x^ {2} and n divides the constant factor 2y^ {2}11y12 One such factor is 2xy
So our equation is exact This time we will evaluate I(x,MATH 106 HOMEWORK 3 SOLUTIONS 1 Using the CauchyRiemann equations, show that if f and f are both holomorphic then f is a constant Solution Let f = uiv,so f = u iv Since they are holomorphic, we can use the CauchyRiemannY 2 − x 2 sin(xy)dy cos(xy) − xy sin(xy) e 2xdx = 0 M = cos(xy) − xy sin(xy) e 2x ∂M∂y = −x 2 y cos(xy) − 2x sin(xy) N = y 2 − x 2 sin(xy) ∂N∂x = −x 2 y cos(xy) − 2x sin(xy) They are the same!




Worked Example Implicit Differentiation Video Khan Academy




If 2x 2 3xy Y 2 X 2y 8 0 Then Dy Dx
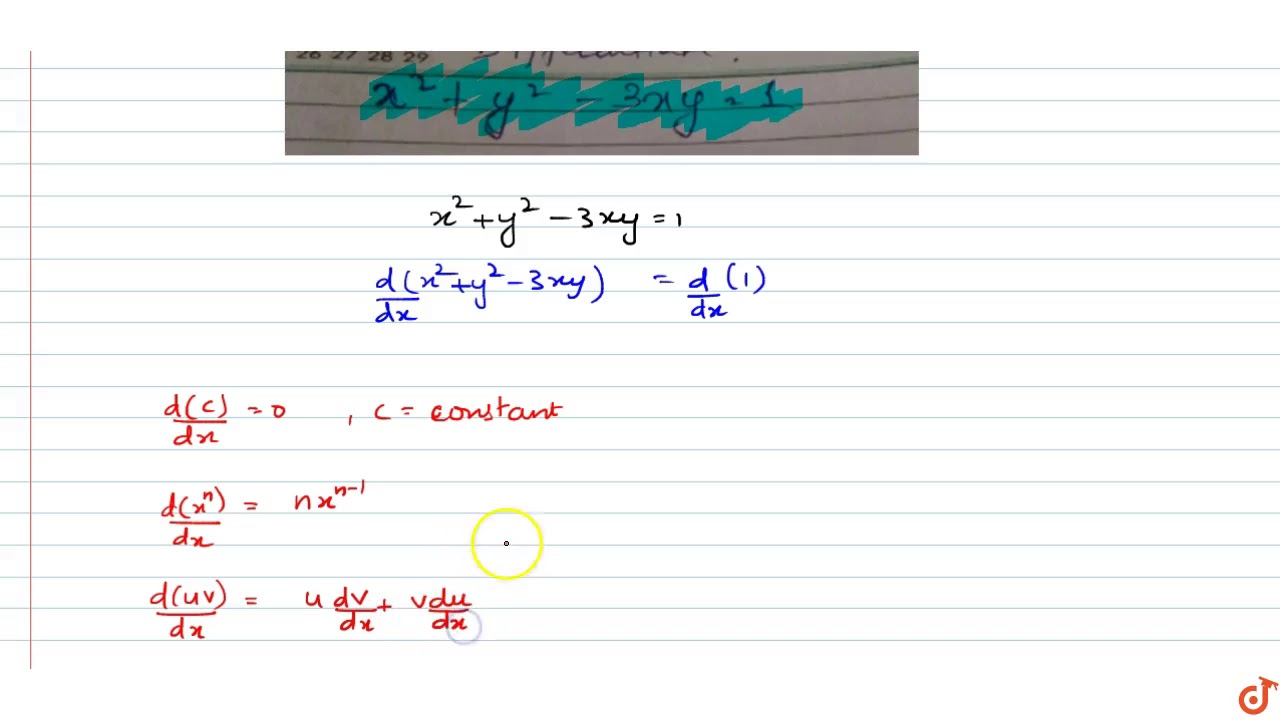
If x,y are integral solutions of 2x 2 3xy 2y 2 = 7, then value of mod(x y) is the person who have asked this is a dumbIf the lines represented by the equation 2x^2 3xy y^2 = 0 make angles α and β with xaxis, then cot^2 α cot^2 βIn other words, no point with x = 0 belongs to the constraint, so we won't get any candidate points x = 2 g x = 2x f y = 1 g y = 2y 5 Set up the Lagrange multiplier equations f x = λg x ⇒ 2 = λ2x (13) f y = λg



If U X 2 3xy Y 2 Verify 2u X Y 2u Y X Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




If 2x Y 5 Then The Maximum Value Of X 2 3xy Y 2 Is
$v(x, y) = 3x^2 y y^3 v(0, 0);An infinite number of combinations for example, when X = 1 and Y = 10 then XY = 10 U(X,Y)=10 X 1 2 4 5 10 Y 10 5 25 2 1 U(X,Y)= X 1 2 4 8 Y 10 5 25 1 The indifference curves look something like thisTest 2, Math Page 1 of 5 Pages Solutions Name (%) 1 Consider the surface x4 2xy y3 z2 exz = 1 and the point P 0(−1,1,0) on (14) that surface Find (a) the tangent plane at P0 The given surface is a level surface of f(x,y,z) = x4 2xyy3 z2 exz We need∇f = (4x3 2y zexz)~i(2x3y2)~j (2z xexz)~k and particularly ∇f(−1,1,0) =−2~i~j−~k
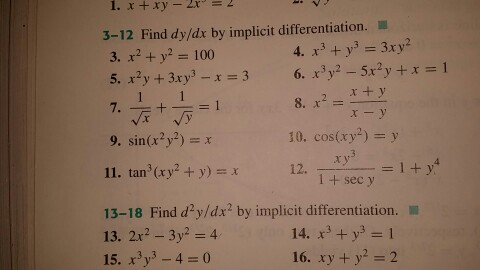



Solved Find Dy Dx By Implicit Differentiation X 2 Y 2 Chegg Com




Maximize F X Y Xy Subject To X 2 Yx Y 2 1 Mathematics Stack Exchange
∂u ∂y = 1/x 1(y/x)2 = x x2 y2 ⇒ ∂2u ∂y2 = −2xy (x2 y2)2 Thus ∆u = 0 and u is harmonic More generally we have the following result Theorem 1 analytic and u,v ∈ C2(Ω), then u and v are harmonic on Ω Remarks 1 The C2 hypothesis is actually unnecessary As we will see, if f is analytic, then Ref and Imf are in fact C∞Factor 2x^23xyy^2 2x2 3xy y2 2 x 2 3 x y y 2 For a polynomial of the form ax2 bx c a x 2 b x c, rewrite the middle term as a sum of two terms whose product is a⋅c = 2⋅1 = 2 a ⋅ c = 2 ⋅ 1 = 2 and whose sum is b = 3 b = 3 Tap for more steps Reorder terms 2 x 2 y 2 3 x y 2 x 2 y 2 3 x y Reorder y 2 y 2 and 3X =(5x2 7y)(2)(2x−4y3)(10x) ∂U ∂y = U y =(5x2 7y)(−12y2)(2x−4y3)(7) Example 5 U = 9y3 x−y Answer ∂U ∂x = U x = (x−y)(0)−9y3(1) (x−y) 2 = −9y3 (x−y) ∂U ∂y = U y = Therefore, at x =2, if x is increased by 001 then y will increase by 004 4 The two variable case If z = f(x,y) then the change in z is dz




If X 3 Y 3 3xy 2 3x 2y 1 0 Then At 0 1 Dy Dx Youtube




100以上 If U X Y X 2 Y 2 2x 3xy Then 1764 Josspix7odk
Fy = −sin(x2 y), fyx = −cos(x2 y)2x d) both sides are f0 (x)g 0 (y) 2 (fx)y = ax6y, (fy)x = 2x6y;\tag{18}$ it is easily checked that such $v(x, y)$ satisfies the CR equations with the given $u(x, y)$; Find all the partial derivatives of the first and the second order for f(x, y) = x^2 3xy^2 2y 5 1) Find fx, fy and fxy for e^2x sin (Piy/3) 3) Find fx , fy , and for x^2 y e^xy^4 5) Find fx (x, y) and fy(x, y) for f(x, Y) = xy/x^2y^2 5) Find an equation of the tangent plane to the surface z = 8?



Www2 Imperial Ac Uk



Legacy Www Math Harvard Edu
• If x = 0, then (9) gives 02 − y2 = 1, but this has no solution!0 Then y 1 (x) c 2 c 1 y 2 (x) = 0 or y 1 (x) = – c 2 1 y 2 (x) = C y 2 (x) Therefore Two functions are linearly dependent on the interval if and only if one ofThis means that a function u(x,y) exists such that du = ∂u ∂x dx ∂u ∂y dy = P dxQdy = 0 One solves ∂u ∂x = P and ∂u ∂y = Q to find u(x,y) Then du = 0 gives u(x,y) = C, where C is a constant This last equation gives the general solution of P dxQdy = 0 Toc JJ II J I Back




If 2x 2 3xy Y 2 X 2y 8 0 Then Dy Dx Youtube



If X Y 2 Then What Is The Value Of X Y 6xy Quora
Example 2 Maximize u =4x2 3xy 6y2 subject to xy =56 Set up the Lagrangian Equation L =4x2 3xy 6y2 λ(56−x−y) Take the firstorder partials and set them to zero L x =8x3y −λ=0 L y =3x12y −λ=0 Lλ =56−x−y =0 From the first two equations we getY(0) = 1;y0(0) = # f(x,y) = 2x^3xy^25x^2y^2 # Let us find the first partial derivatives # (partial f) / (partial x) = 6x^2y^210x# # (partial f) / (partial y) = 2xy2y# So our critical equations are # 6x^2y^210x = 0# # 2xy2y = 0# From the second equation we have # 2y(x1) = 0 => x=1,y=0# Subs #x=1# into the First equation and we get



Www3 Nd Edu



1
Multiplying both sides by x one obtain the equation M (x,y)dx N (x,y)dy =0, with M (x,y) = 3x^2y xy^2 , N/x,y) = x^3 x^2y Now we have an exact equation because dM/dy = dN/dx = 3x^2 2xy We know that exist the general integral F (x,y) = C such that (1) dF/dx = M = 3x^2y xy^2 (2) dF/dy = N = x^3 x^2y Explanation differentiate implicitly with respect to x the term 3xy is differentiated using the product rule ⇒ 2x 3(x dy dx y1) 2y dy dx = 0 ⇒ 2x 3x dy dx 3y 2y dy dx = 0 ⇒ dy dx (3x 2y) = −2x − 3y ⇒ dy dx = − 2x 3y 3x 2yU(x, y) =min(2X, 3Y) This is an example of perfect complements The MRS is undefined at the vertex where 2X=3Y But lets graph the indifference curve, remember they L shaped We need to find the corner point To do this set the two elements of in the utility function equal to each other so there is no extra X or Y being consumed that




Solved A Harmonic Conjugate Of U 2x X3 3xy2 Is Select Chegg Com




Systems Of Equations With Elimination 4x 2y 5 2x Y 2 5 Video Khan Academy
(c) ux 2uy (2x−y)u= 2x2 3xy−2y2 We let η= y−2xand ξ= x So y= η2ξ Then we have uξ −ηu= 5ξη−2η2, eξηu ξ = (5ξη−2η2)eξη, u= 5ξ−2η− 5 η eξηf(η), u= 9x−2y− 5 y−2x f(y−2x)exy−2x2 2 Consider the equation 3uy uxy = 0 (a) What is its type?F yy=−xsin(y)S((−1)n1;nˇ) =−(−1)n1 sin(nˇ)=0 So the Hessian matrix at ((−1)n1;nˇ) is 0 (−1)n (−1)n 0 with determinant D=−(−1)2n =−1U(x,y) = x3 −3xy2 is harmonic To find a harmonic conjugate v of u, we must have u x(x,y) = v y(x,y) and u y(x,y) = −v x(x,y) From the first we have v y(x,y) = 3x2 −3y2, from which it follows that v(x,y) = 3x2y −y3 ϕ(x) for some function ϕ of x It now follows from the second equation that −6xy = −v x(x,y) = −(6xy ϕ0(x)), and so ϕ0(x) = 0 Hence for any real number c, the function



Differentiate X 2 Y 2 3xy 1 Youtube
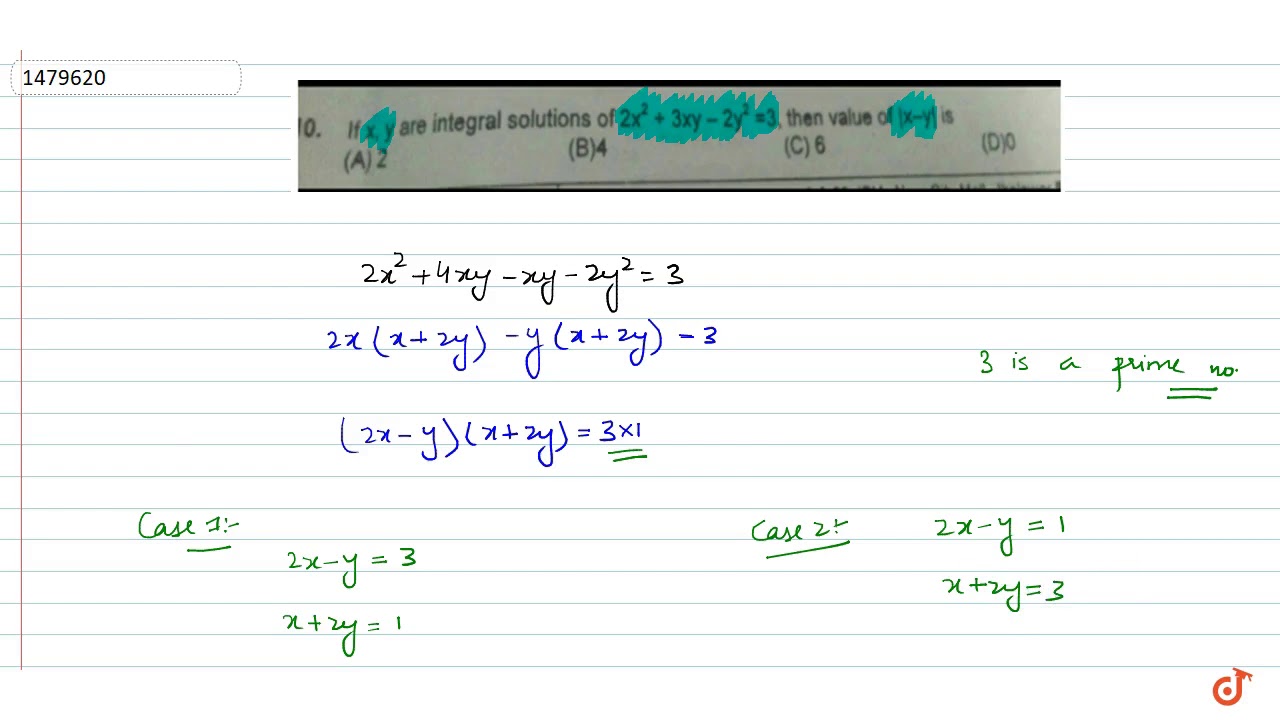



If X Y Are Integral Solutions Of 2x 2 3xy 2y 2 3 Then Value Of X Y Is Youtube
Find dy/dx x2xyy^2=2 Differentiate both sides of the equation Differentiate the left side of the equation Tap for more steps Differentiate Tap for more steps By the Sum Rule, the derivative of with respect to is Differentiate using the Power Rule which states that is whereProjection of the surface, S, onto the x−yplane is given by D = {(x,y) x2 −2xy2 = (x−1)2 y2 ≤ 1} Hence the area of S is given by Z Z S 1dS = Z Z D 1 7 6 dxdy = 7 6 Z Z D 1dxdy = 7 6 × Area of D = 7 6 π Note, since D is a cricle or radius 1 centred at (1,0) the area of D1 TRUE or FALSE There is a function f R2!R such that @f @x = y and @f @y = x2 Solution FALSE (If there were such a function, then its mixed second partial derivatives would be @ 2f @y@x = 1 @f @x@y = 2x These functions are continuous and unequal, but by Clairaut's Theorem, if a function has continuous second partial derivatives then its




100以上 If U X Y X 2 Y 2 2x 3xy Then 1764 Josspix7odk




Solved 7 F X Y X Y Subject To X 2 Xy Y 2 Chegg Com
I've learned through youtube and other online sources This is a separable differential equation, so you should get the x's and y's on opposite sides and then integrate 3yxdxx^2 (y^22y)dy=0 add the subtracted expression to both sides 3yxdx=x^2 (y^22y)dy divide by y on both sides 3xdx=x^2 (y2)dy if 2x^23xyy^2x2y8=0 then (dy)/(dx) Updated On 132 To keep watching this video solution for FREE, Download our App Join the 2 Crores Student community now!If 3 By 2 Plus I Root3 By 2 Power 50 Equal 3 25 X Iy Where X And Y Are Real Then The Ordered Pair X Y Is If 3 sin (xy) 4 cos (xy) = 5, then dy/dx = If 3 Tan Theta Tan Phi Is 1 Then If 3 x = 4 x1, then x is equal to If 3x y k = 0 is a tangent to the circle x 2 y 2 = 10, then the values of k are If 4 Sin Inverse X Plus Cos Inverse X




If U Sin 1 X 2 Y 2 X Y Then Show That X Du Dx Y Du Dy Tan U Mathematics 1 Question Answer Collection



If X Y X Y X Y 3xy Then What Is X And Y Mathematics Solutions
Function f(z) = u(x;y) iv(x;y) in terms of zonly 8Verify that the following functions, denoted by u, of real variables xand y are harmonic and nd their harmonic conjugate If fis given by f(z) = u(x;y)iv(x;y) is entire then nd f(z) in each case (a) u(x;y) = y3 3x2y (b) u(x;y) = sinhxsiny最高のコレクション if u (x y)=x^2 y^2 2x3xy then 10 Find the extreme values of f (x,y) = 2x2 3y2 −4x−5 on the region D = { (x,y) x2 y2 ≤ 16} Solution We first need to find the critical points These occur when f x = 4x−4 = 0, f y = 6y = 0 so the only critical point of f is (1,0) and it lies in the region x2 y2 ≤ 16 On the circle x 2y = 16, we have y2 = 16−x2 and g (x) = f (x,JacobianNow, sin(y)=0 when y=nˇ, for all integers n Then setting 1 xcos(nˇ) =1 (−1)nx=0, we get that critical points are (x;y)=((−1)n1;nˇ) for n∈Z At these points f xx≡0;




Partial Differentiation If U X 2 Y 2 Z 2 X E T Y E Tsint Z E Tcost Prove That Du Dt 4e T Youtube



8c0dzdxgcdzq M
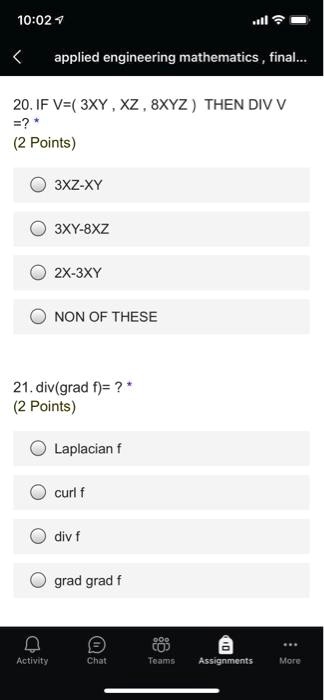
2 Divergence (Div) If F(x,y) is a vector field, then its divergence is written as divF(x,y) = ∇·F(r) which in two dimensions is ∇·F(x,y) = (∂ ∂x i ∂ ∂y j)·(F 1(x,y)iF 2(x,y)j), = ∂F 1 ∂x ∂F 2 ∂y It is obtained by taking the scalar product of the vector operatorLemma 54 Let z= x iyand suppose that f(z) = u(x;y) iv(x;y) is analytic Then the dot product of their gradients is 0, ie rurv= 0 Proof The proof is an easy application of the CauchyRiemann equations rurv= (u x;u y) (v x;v y) = u xv x u yv y= v yv x v xv y= 0 In the last step we used the CauchyRiemann equations to substitute v yforSubject to the constraint 2x2 (y 1)2 18 Solution We check for the critical points in the interior f x = 2x;f y = 2(y1) =)(0;
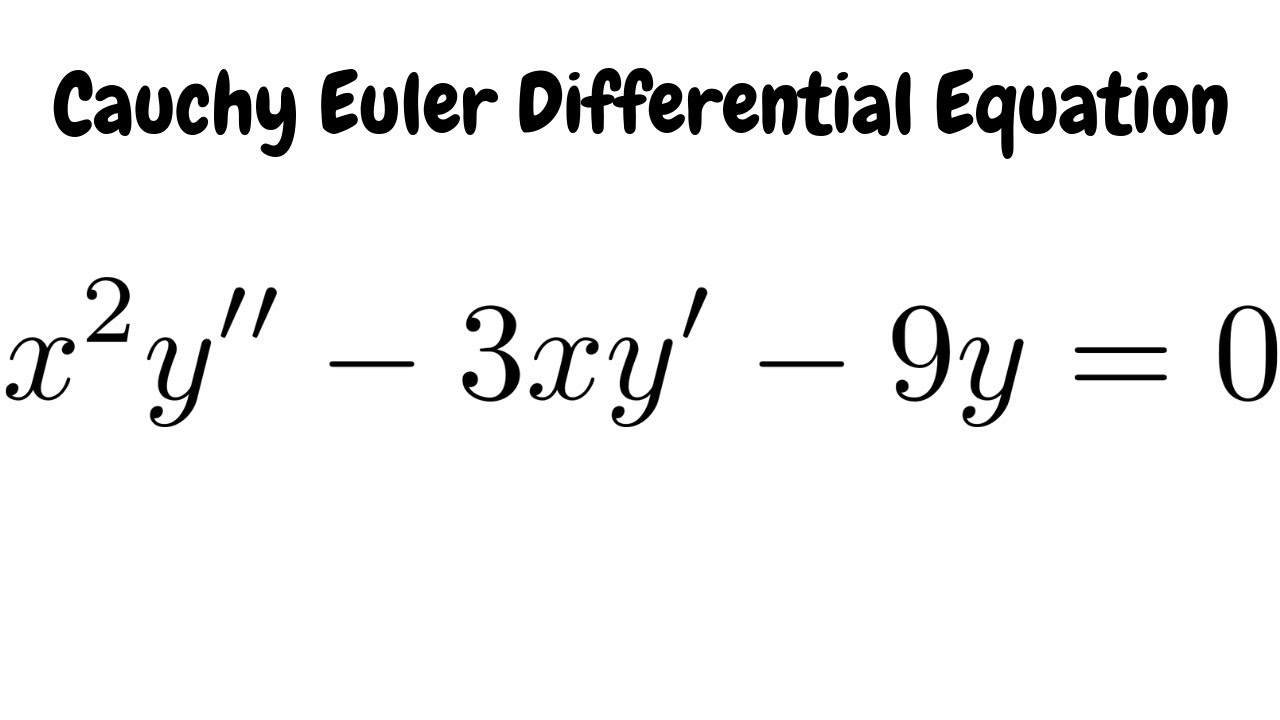



Solve X 2y 3xy 9y 0 Cauchy Euler Differential Equation Youtube



1
3xy= x y2 SOLUTION This is a Bernoulli equation Multiplying through by y2 gives y2y0 3xy3 = x Let v= y3 Then v0= 3y2y0, or 1 3 v 0= y2y0 Therefore, we get 1 3 v0 3xv= x ) v0 9xv= 3x which is linear in v 4 Obtain the general solution in terms of , then determine a value of so that y(t) !0 as t!1 SOLUTION y00 y0 6y= 0;Watch Video in App This browser does not support the video element 448 k 22 k Answer Step by step solution by experts to help you in doubt clearance & scoring(c) Suppose a point has coords X=1, Y=2 wrt basis u,v Find the value of q at the point two ways, using its X,Y coordinates and then again using its x,y coordinates 6 Start wit hq=x 2 3xy5y2 and make the change of variable X=xy Y=xy (a) Find q in terms of X and Y just with algebra (b) What new basis is involved when you use variables



People Whitman Edu



If X 2 3xy Y 2 60 Where X And Y Are Real Determine The Maximum Possible Value Of Xy Quora
∂2 f ∂x2 = (1 xy)(3y) y 1 3xy) = 4y 6xy2 (1610) ∂2 f ∂y∂x = (1 xy)(3x) x 1 3xy) = 4x 6x2y (1611) ∂2 f ∂x∂y = 4x (1 xy) 2x2y 4x 6x2y (1612) ∂2 f ∂y2 = 2x2 (x) 2x3 Notice that the second and third lines are equal This is a general fact the mixed partials (the middle terms above) are equal when the secondTherefore fxy = fyx a = 2 By inspection, 2 2 ⇔ one sees that if a = 2, f(x,y) = x y 3xy is a function with the given fx and fy 2A5Solution In terms of x;y, we can write f(z) = x2 y2 So, u(x;y) = x2 y2 and v(x;y) = 0 The partial derivatives are u x = 2x v x = 0 u y = 2y v y = 0 The CauchyRiemann equations become 2x= 0 2y= 0 Thus, CR hold only at the origin Since the partial derivatives exist in a neibhbourhood of the origin and are continuous at the origin (in




Solve The Equation X 2 3xy Y 2 Dx X 2dy 0 Given That Y 0 And X 1



Ex 9 5 15 Class 12 Find Solution 2xy Y 2 2x 2 Dy Dx 0 When
v y = u x = 3 x 2 2 y − 4 y 2 and after integration v ( x, y) = 3 x 2 y y 2 − ( 4 / 3) y 3 β ( X) and after trying to solve for β I found it equal to β = x 2 y − x 2 and after applying it to the v ( x, y) = 4 x 2 y 2 = ( 4 / 3) y 3 − x 2 which in obviously is not applying CR equations if we want to prove the solutionThus $f(z) = f(x, y) = u(x, y) iv(x, y) = (x^3 = 3x^2y) i(3x^2 y^3 v(0, 0)) \tag{19}$ is a holomorphic function of $z = x iy$ Example 1 Find each of the directional derivatives D→u f (2,0) D u → f ( 2, 0) where f (x,y) = xexy y f ( x, y) = x e x y y and →u u → is the unit vector in the direction of θ = 2π 3 θ = 2 π 3 D→u f (x,y,z) D u → f ( x, y, z) where f (x,y,z) = x2zy3z2 −xyz f ( x, y, z) = x 2 z y 3 z 2 − x y z in the direction of →v




Solved Find The Points On The Curve X 2 3xy Y 2 5 That Chegg Com



Verify Euler S Theorem For The Function U X 3 Y 3 3xy 2 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
U,, x2x 1 y for all real and y Then a function v yx, so that f z yu y i v x, is analytic, is a) x 2 2 y 1 b) 2 x 1 2 y c) 2 x 1 2 y d) x y C2 21 12 At the function a) is analytic b) differentiable c) doesn't satisfy CR equation d) Satisfy CR equations but not differentiable 13Uiv ANSWER Easy to show uxx uyy = 0, so u is harmonic Let v be the conjugate harmonic function Then vy = ux = 2¡3x2 3y2 Thus v(x;y) = 2y¡3x2yy3 `(x) Now vx = ¡6xy`0(x) = ¡uy = ¡6xy Thus `(x) =constant, so v(x;y) = 2y¡3x2yy3 constant and u iv= 2z¡z3 ic, where cis a real constant (Note that we have expressed this in terms of z= xiy) 1




X 3 3xy 2 Dx Y 3 3x 2y Dy Youtube



Ualberta Ca




2 X 2 3xy Dy Y 2 2xy Dx 0 Brainly In




The Equation3y 3xy 2x2 2y2x2 Can Be Written In The Form Y F Y X I E It Is Homogeneous Brainly Com



If U X 2tan 1 Y X Y 2tan 1 X Y Prove That 2u Y X X 2 Y 2 X 2 Y 2 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community



If U X Y Z Xy 2z 3 X Sin T Y Cos T Z 1 E 2t Find Du Dt Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




Solved Solve Each System Use Any Method You Wish 2x 2 Chegg Com




Chapter 7 Calculus Of Several Variables




Math 535a Homework 4 Solutions Math 535a Differential Geometry Studocu



Jntua Ac In



Solved Exercises 1 Show That X Y Is Harmonic In Some Chegg Com




6 7 Maxima Minima Problems Mathematics Libretexts




15 3 Line Integrals Over Vector Fields Chapter 15 Vector Analysis Part Calculus Iii




Solved A Table Of Values For The Wind Chill Index W F T V Is Given In Exercise 14 3 3 On Page 923 Use The Table To Estimate The Value Of D U F 30



Differential Equations



Algebraic Geometry A New Treatise On Analytical Conic Sections F The Following Hyperbolas 1 2x 3xy 2y 6 2 3x Iy L2x 8y 1 0 3 2x 3y Xy Ix Y L0 0 I 5x 3y Lt 2xy 4x Iy I 0 5 Find The Equation Of




Solutions To Implicit Differentiation Problems
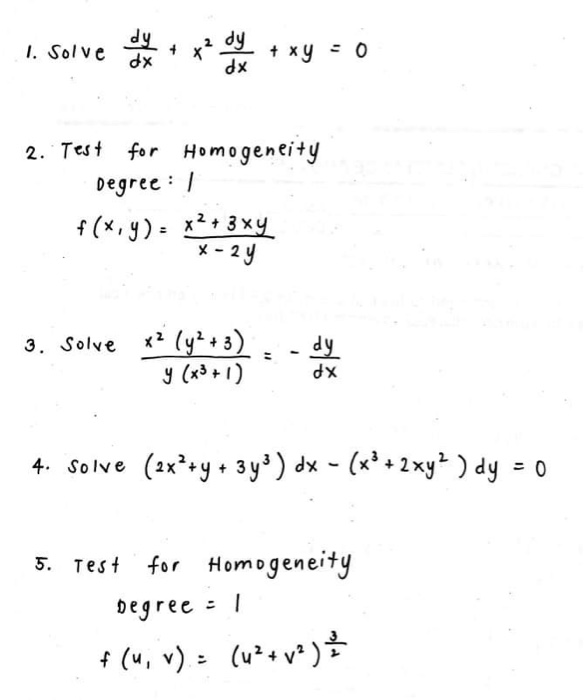



Solved 1 Solve Dy Dx 뿄 X Du Je 뿄 Xy 0 2 Test For Chegg Com




Find The Directional Derivative D U F X Y Of The Function F X Y X2 3xy Homeworklib



Whitman Edu




Verify Stokes Theorem For V Zi Xj Yk Over The Hemispherical Surface X 2 Y 2 Z 2 1 And Z Gt 0 Mathematics Stack Exchange




Find Dydx Where X 2 Y 2 3xy 1




If X Y Are Integral Solutions Of 2x 2 3xy 2y 2 7 Then Value Of X Y Is



Math Dartmouth Edu




Ex 5 3 6 Find Dy Dx In X3 X2y Xy2 Y3 81 Cbse



How Do You Find All Points On The Curve X 2 Xy Y 2 7 Where The Tangent Line Is Parallel To The X Axis And The Point Where The Tangent Line



Prove That F X Y X 3 2x 2y 3xy 2 Y 3 Is Homogeneous What Is The Degree Verify Euler S Theorem For F Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




Solved 1 Find And Sketch The Domain Of The Following Chegg Com




For What Value Of N Is Following A Homogeneous Differential Equation



Implicit Differentiation




If X 2 Y 2 3xy Then Choose The Correct Answer Of 2log X Y Form The Following Option




Ex 5 3 6 Find Dy Dx In X3 X2y Xy2 Y3 81 Cbse



The Two Curves X 3 3xy 2 2 0 And 3x 2y Y 3 2 0 Youtube




11 Business Math Stats Vol 2 Em Pages 51 100 Flip Pdf Download Fliphtml5




Multivariate Functions And Partial Derivatives Sage Research Methods



Chapter 1 Partial Differential Equations Ppt Video Online Download
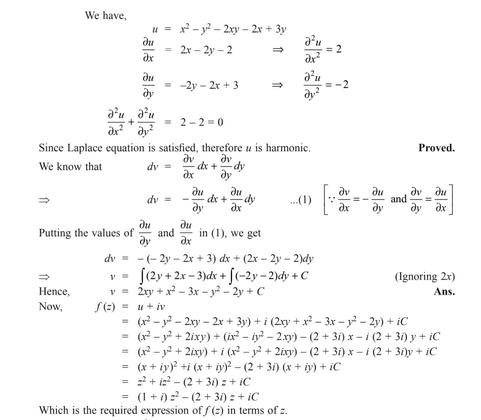



Prove That U X 2 Y 2 2xy 2x 3y Is Harmonic And Find Harmonic Conjugate V Edurev Iit Jam Question



Hw 1
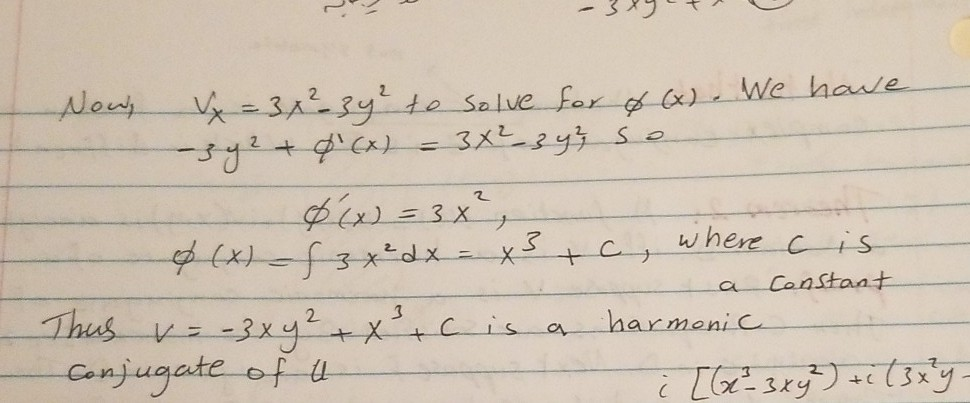



Solved Exercises 1 Show That U X Y Is Harmonic In Some Chegg Com




Rd Sharma Solutions For Class 8 Chapter 6 Algebraic Expressions And Identities Download Free Pdf



How To Solve X 3 3xy 2 Dx 3x 2y Y 3 Dy Quora
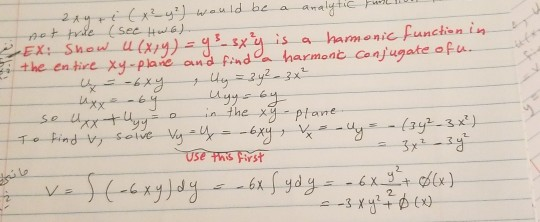



Solved Exercises 1 Show That U X Y Is Harmonic In Some Chegg Com
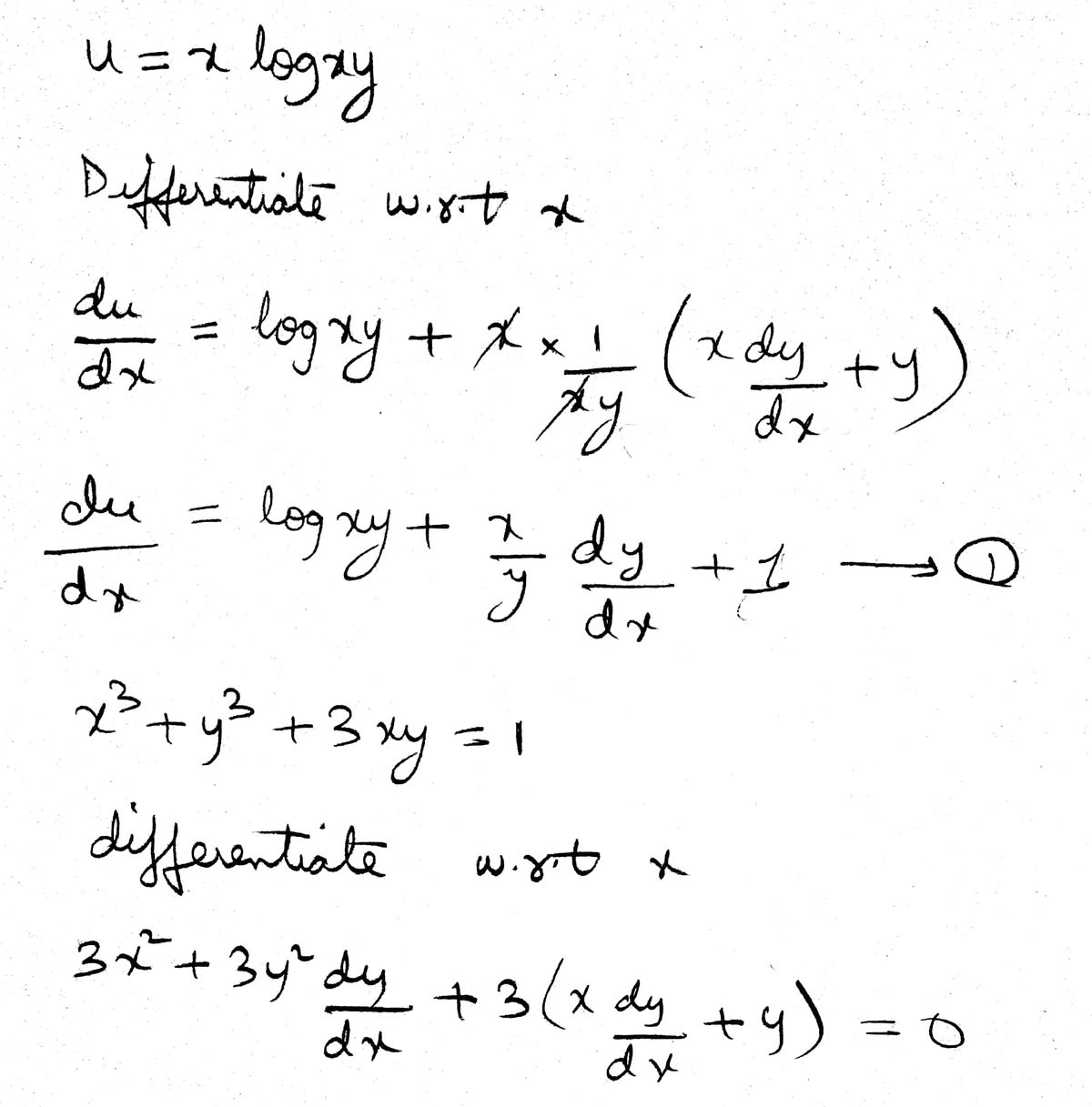



Answered If U X Log Xy Where X3 Y3 3xy 1 Find Bartleby




If X 2 Y 2 3xy 0 And X Gt Y Then Find The Value Of Log Xy X Y




Answered Solve The Homogeneous Equation X Bartleby




Doc Partial Derivative Mcq S Assignement Innocentboy Nishant Academia Edu




11 Business Math Stats Vol 2 Em Pages 51 100 Flip Pdf Download Fliphtml5




If X Y 2 3 Find The Value Of 3x 2y 2x 5y Dot



Wright Edu




Solved Let F X Y X 3 3xy 2 2y 3 Show That The Chegg Com




Prove That X2 Y2 C X2 Y2 2 Is The General Solution Of The Differential Equation X3 3xy2 Dx Y3 3x2y Dy Where C Is Parameter Mathematics Shaalaa Com




Solved Given Systems Of Nonlinear Equations 2xy X Y 0 X2 Xy 0 Which Is The Correct Jacobian Matrix J For The Above System 2y 3x 2x X J 2x 2y 3xy 2x Y J 2r R 2y 3ry 2x



Pnw Edu




If 4x 2 Xy 3xy Y 2 12 5 Find X 2y 2x Y Brainly In




Solved Verify That The Differential Equation 3xy Y 2 Chegg Com



Can You Help Solve This Question If X 3 2 3 2 Xy 1 Then Prove That I X 2 Y 2 98 Ii X 3 Y 3 970 Iii X 2 Xy Y 2 99 Quora




Vector Analysis By Alimkanwalimtinaa Issuu



Math Uakron Edu




Linear Algebra Sheet 5 Summer 19 Warning Popup Annotation Has A Missing Or Invalid Parent Studocu



If X 2 3xy Y 2 60 Where X And Y Are Real Determine The Maximum Possible Value Of Xy Quora



3 8 Implicit Differentiation Calculus Volume 1



Tau Ac Il




If U Log X 2 Y 2 Z 2 Verify 2u X Y 2u X Y



Web Williams Edu



Find An Analytic Function Whose Real Part Is U X 3 3xy 2 3x 2 3y 2 3y 2 1 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
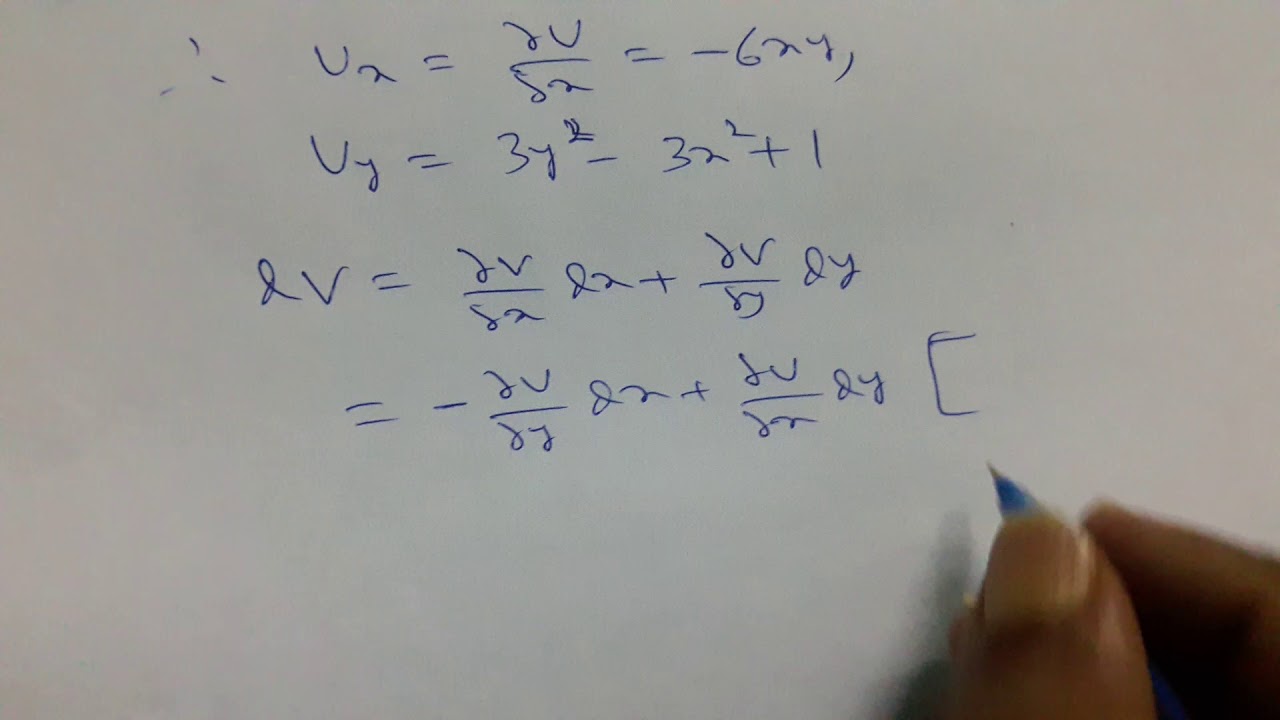



If U X Y Y 3 3x 2 Y Y Determine V X Y So That F U Iv Is An Analytic Function Youtube




Misc 4 Prove X2 Y2 C X2 Y2 2 Is General Solution Of




7 The Hcf Of Left 1 Point 1r See How To Solve It At Qanda



Apsva Us




Chapter 5 Partial Differentiation




Solved Exercises 1 Show That U X Y Is Harmonic In Some Chegg Com




If X 2 And X Square Y Square 3xy 5 Then Find Y Brainly In



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿